Compare the contents of two databases and copy rows from one database to another. You can also compare the structure of the databases.
- Select System | Databases |
 Maintenance >
Maintenance >  Compare and merge.
Compare and merge.
- Select the databases and comparison settings in the dialog box, and click Compare.
Dialog Box Options
- Databases
- Click Select to select Db1 and Db2 databases to compare.
- Relation
- The rows of databases are compared based on the relation. The relation key can be the value of a single field, the combined value of multiple fields, or the row id, $RID. If no relation is defined, you can still view, edit, and copy rows between databases, but without comparing and synchronizing the corresponding rows.
- You can select $RID as the relation key from the Relation 1 and Relation 2 lists. Other fields to select from the lists depend on the properties you select:
- Select from the common fields - The list collects database fields that are found in the structure of both databases.
- Select from the fields having unique contents - The list collects database fields whose content is unique.
If both properties are selected, the lists collect common fields from the databases whose content is unique.
- You can also select any field in the database as the relation key by clicking Select from database. The database fields and their contents open in a list view. Click the desired field. If you want to use the combined value of multiple fields as the relation key, click Add from database, and select another field. The field names appear in the Relation 1 / Relation 2 field separated by a vertical bar (|).
- Compare content
- To compare and merge the contents of databases, select Compare content and click Compare.
- The contents of the databases open in a list view in a comparison window. Other options under Compare content:
- View side by side: The list views are side by side in the comparison window. When the option is empty, the list views are on top of each other.
- Show unfilled values (--): Hyphens are added to fields that have no value.
- Compare: The contents of the databases are compared, and you can also select the following options:
- Show only different rows - Recommended for large databases.
- Treat empty and unfilled values (--) as equal
- Do not compare time stamp field SYSTEMTIME - A field where the program automatically writes the date and time whenever the contents of a row have been changed.
- The order of the database fields in the view from left to right:
- Fields used as a relation.
- Other common fields.
- Fields that exist only in that database.
- The fields in each group are in alphabetical order.
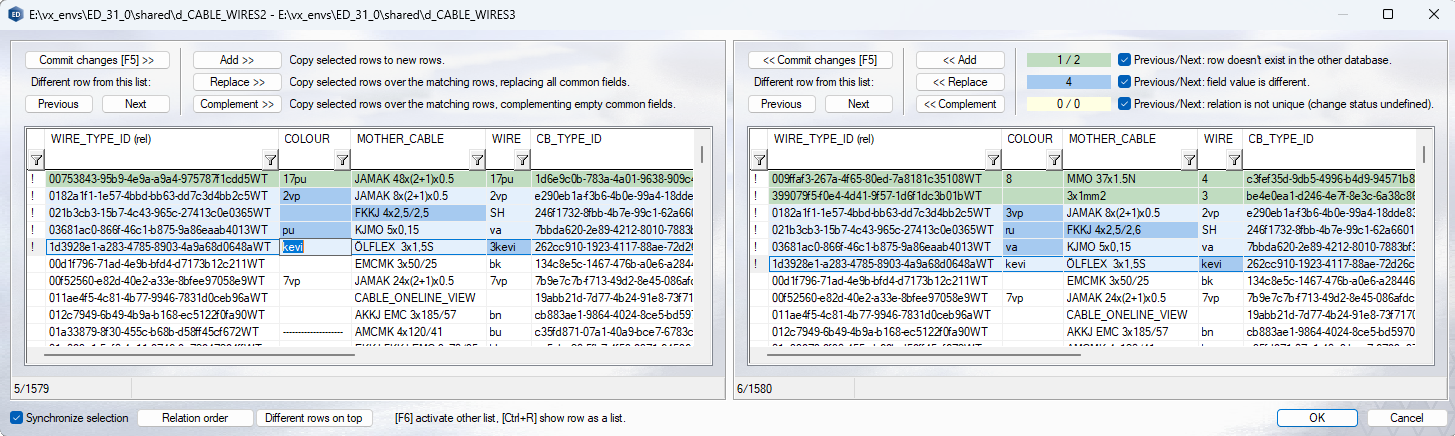
- The field used as a relation is marked in the column header with the string (rel), and a unique field with the string (uni):


- Fields that exist only in one database are marked in the column header with the string (db1) or (db2).

- Similar rows in the database appear on a white background. Rows with differences are marked with a green, blue or yellow background in the list views. The number of differences is displayed above database Db2.
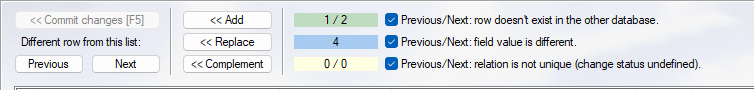
- Green background: number of rows in database Db1 that are not in database Db2 / number of rows in database Db2 that are not in database Db1.
- Blue background: number of rows where the field value is different in database Db1 and Db2. In the list view, the row is highlighted in light blue, the different field in darker blue.
- Yellow background: the relation is not unique. In one of the databases, there is more than one row with the same value in the relation field. In this case, the status of change is undefined - the contents of the fields are not compared.
- When the Previous/Next check box is selected, you can browse rows with those differences by clicking Previous or Next. When a row is selected in either database, you can choose from the following options:
- Commit changes: the row is copied to the other database as a new row, if it does not exist. If a corresponding row exists in the other database, it is copied over it.
- Add: the row is always added as a new row to the other database.
- Replace: the row is copied over the corresponding row.
- Complement: the row is copied over the corresponding row, but only over fields that are empty in the other database.
-
Note: Select multiple rows while holding down the Ctrl key. Select a set of rows:
- Click the first row.
- Press the Shift key, and click the last row of the set.
- When you select a row, the corresponding row is also selected in the other database if Synchronize selection is enabled.
- When Synchronize selection is disabled, you can select rows individually. Commit changes is not available, but you can use the Add, Replace, and Complement functions. Replace and Complement are based on the current selection mode.
-
Note: The program forces a field defined as UNIQUE to be filled in before the dialog box can be closed by saving the changes. When you edit a database by copying a row, the value of a unique field is not copied, but remains blank. These fields appear highlighted in red.
- To sort the list views by relation field value, click Relation order.
- Different rows on top places the lists in their original order, different rows to the top of the list view.
- Compare structure
- To compare the database structures, select Compare structure and click Compare. The structure of the databases opens in a list view in the comparison window. Other options under Compare structure:
- Compare field types
- Text field A or T (UNICODE)
- Alphanumeric field B or M (UNICODE).
- Numerical field N.
- Compare field lengths
- Compare field indexing
- Blank - no indexing
- IND - indexed field
- UNIQUE - indexed, unique field
- Compare field order
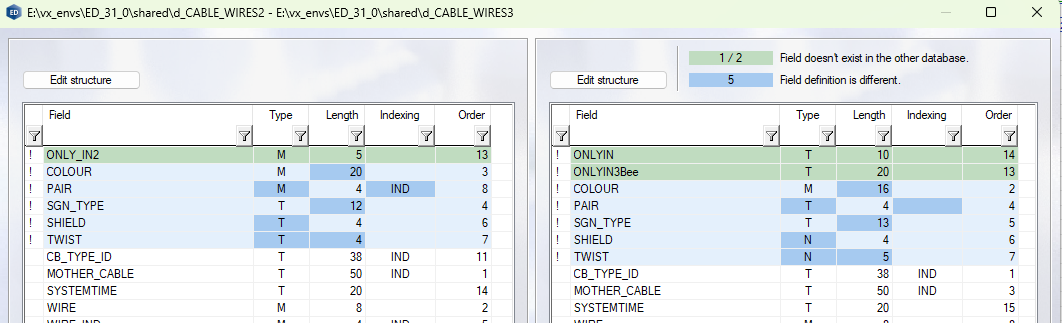
- Similar fields in the database appear on a white background. Fields with differences are marked with a green or blue background in the list views. The number of differences is displayed above database Db2.
-
- Green background: number of fields in database Db1 that are not in database Db2 / number of fields in database Db2 that are not in database Db1.
- Blue background: number of fields where the field definition (type, length, indexing, order) is different in database Db1 and Db2. In the list view, the field row is highlighted in light blue, the different definition in darker blue.
- In the list view, you can edit the database structure by clicking Edit structure.
- Define the Structure of a Database
- To sort the list views by relation field value, click Relation order.
- Different rows on top places the lists in their original order, different rows to the top of the list view.
- Clear history
- Clear the history of database selection lists. The selection history is stored in the user folder.
 Maintenance >
Maintenance >  Compare and merge.
Compare and merge.





