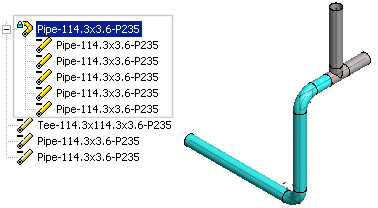
Route a Pipeline
Piping Design
Model a pipeline by sketching the pipe routing. A pipeline is formed from pipe components, which comprise pipes and pipe parts. As an example, straight pipe and curve.
- Model a Pipeline along a guiding line.
 Model a Pipeline Along a Guide Curve
Model a Pipeline Along a Guide Curve - Add a pipeline by defining the route of the pipe's centerline by clicking points.
- The direction of a pipeline added in the vertical direction (Z axis) will be automatically fixed.
- A pipe part (elbow) will be automatically added between pipes in places where the pipeline's direction changes.
- Model the pipeline close to the actual dimensions. Refine the pipe lengths and their relative positions using geometric constraints.

- Create a new assembly.
 New Assembly to Archive
New Assembly to Archive - Select from the following options.
- On the
 tab, in the Add group, select
tab, in the Add group, select  Add pipeline. (G4)
Add pipeline. (G4) - On the
 tab, in the Pipes group, select
tab, in the Pipes group, select  Add Pipeline (G4 Plant).
Add Pipeline (G4 Plant).
- On the
- Select from the following options.
- Select in the
 Properties group Material, Pipe Diameter, Wall Thicness, and Bend radius. (G4)
Properties group Material, Pipe Diameter, Wall Thicness, and Bend radius. (G4) - Select in the
 Properties group Pipe Class, Nominal size, Wall Thickness, Pipe Item, Curve Item (G4 Plant).
Properties group Pipe Class, Nominal size, Wall Thickness, Pipe Item, Curve Item (G4 Plant).
- Select in the
- Select either of the following:
- Select
 Using Elbows for the places where the pipeline's direction changes.
Using Elbows for the places where the pipeline's direction changes. - Select
 Using Bending for the places where the pipeline's direction changes.
Using Bending for the places where the pipeline's direction changes.
- Select
- Click the start point of the pipe's centerline.
- Enter the line position to be used.
- Define the sweep plane in one of the following ways:
- Select the draft layer by the context-sensitive function, for example
 Horizontal (XY) layer, or press Shift+O.
Horizontal (XY) layer, or press Shift+O. 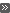 Sweep Plane
Sweep PlaneThe plane lock is enabled until you release it with the F key or select another lock.
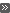 Sweep Plane Based on a Line
Sweep Plane Based on a Line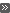 Sweep Plane Based on a Planar Face
Sweep Plane Based on a Planar Face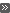 Sweep Plane Based on Three Points
Sweep Plane Based on Three Points
- Select the draft layer by the context-sensitive function, for example
- Define the sweep direction in one of the following ways:
- Constrain the cursor into a ruler.
- Select the sweep direction with a context-sensitive function, for example X Axis Direction.
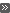 Planar Face Normal as a Sweep Direction
Planar Face Normal as a Sweep Direction Line as a Sweep Direction
Line as a Sweep Direction
- Do either of the following:
- Enter a length for the pipe on the keyboard.
- Before clicking a point you can snap the cursor into a Point, Line or Face on the model if the Snap function is active.

To a Point, Line or Face when the Snap function is active.
- Click a pipeline point. Continue modeling the pipeline by clicking the next point. In the routing points, select bending radius of the curve on the
 tab Properties group field.
tab Properties group field. - When routing the line you can add a component by pressing the B key. Continue routing by confirming the component position by selecting Confirm.
- Undo the previous point by pressing Ctrl+Z , and click the point again. You can undo the added points of the same pipeline all the way to the starting point.
- Select Confirm.
 Browser - Archives
Browser - Archives Auxiliary Modeling Functions
Auxiliary Modeling Functions
Note:
- Pressing the K key shows the directions of the coordinate axes at the cursor.
- The first pipe component added to an assembly is fixed in place, indicated by the lock symbol
 . The component's location will not change if you drag other components of the pipeline. The length of the fixed component will change unless it is defined with a dimension constraint. You can fix and release components using the F key.
. The component's location will not change if you drag other components of the pipeline. The length of the fixed component will change unless it is defined with a dimension constraint. You can fix and release components using the F key.
- If you do not define the position or length of a pipe component accurately when it is modeled, it will be positioned in the assembly using geometric constraints.
- You can also model a pipeline by adding pipes and pipe parts from the component library.
- If you are routing a pipeline using bent pipes, the pipe sections of the pipeline form a single entity. The pipe sections are grouped into a kind of a subassembly within the assembly tree. Bent pipe sections are listed as single rows in the parts list.