Surface Modeling
Surface modeling allows the modeling of unusual shapes. You can utilize the shapes of surrounding parts when modeling a part. You can copy, add and delete surfaces. You can also complement the geometry of parts imported into Vertex using surface modeling functions.
What is a surface model?
A model is handled as a surface model, if the volume created by the model surfaces is not closed. Then the surface model functions can be selected, and use of the some general modeling functions is prevent. When you begin modeling from scratch, general modeling functions and surface modeling functions are available for the creation of the first surface.
The type and shape of the face are determined by the lines you selected to form the face. The result can be a planar surface, perforated planar surface, cylindrical surface, ruled surface, or a spline surface. Line elements selected for a surface are highlighted in the model. Surfaces can also be copied.
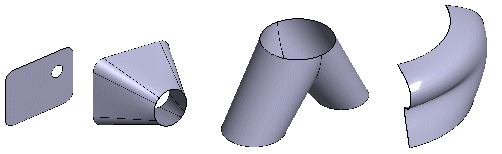
You can perform sketch-based procedures on a surface model in the same way as on a closed volume. You can add roundings and bevels to a surface model. If necessary, you can directly convert a surface model to a sheet-metal part, allowing you to use sheet-metal design functions after defining its thickness. The surface model can be import to the assembly, and create the drawing from the surface model. A sheet-metal type surface model can be flattened.
Creating a volume from a surface model
You can create a closed volume from a surface model in the following ways:
- Using the Tangential Offset function.
- Using the To Volume function.
- Modeling the surfaces required to close the volume.
