Model a Cross Section Valid for Profile Library
General requirements and comments on the model
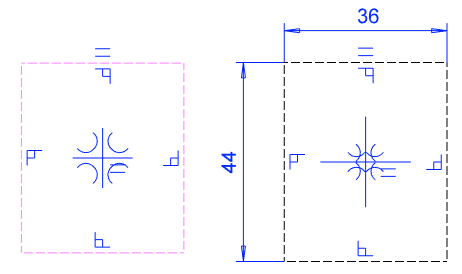
 Create the only sketch of the model To horizontal (XY) plane.
Create the only sketch of the model To horizontal (XY) plane.- The origin of the sketch will be the default reference point of the profile feature.
- Add the necessary guide lines, as their endpoints can be used as other reference points when adding the profile.
- Add density to the model to calculate the correct weight for the profiles.
- Add rendering material to the model if you want the profile to look real.
- This is important at least for wooden profiles, such as boards and panels.
 Do not add other features to the model.
Do not add other features to the model.- If the model has other features, you cannot save the model to the profile library.
- Do not add a grip point to the model that is otherwise used for library features and components.
- Instead of a grip point, the origin of the model and the direction of the Z axis determine the location of the feature.
Model a profile feature valid for library
- Start creating a new part.
- If you wish to save the part in the archive, enter a label for the part.
- The feature will be named when the profile feature is saved in the library. The name can be different from the part label.
- Select the context-sensitive function
 New Sketch> Horizontal(XY) Plane.
New Sketch> Horizontal(XY) Plane.- The origin of the sketch will be the default reference point of the profile feature.
- The normal of the cross section face will be parallel with the Z axis. When modeling a profile part in an assembly, the normal of the cross section will be parallel with the guide curve.

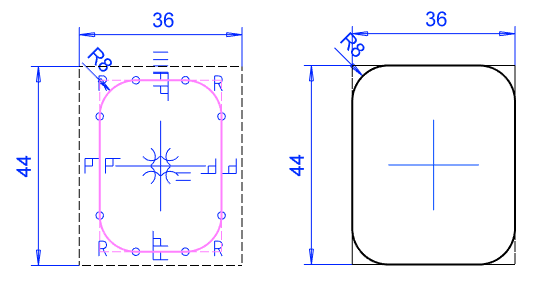
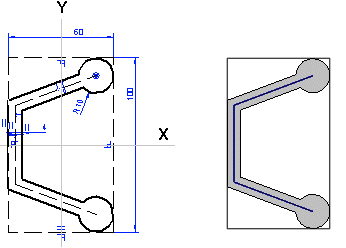
- Draft the sketch of the profile cross section with shape lines.
- The sketch is a closed polyline.
- Draw the web of the profile vertically in the direction of the Y axis.
- Add guide lines in the same sketch for positioning the feature.
- You can select points from the guide line for alternate reference points for the profile feature.
- Add geometric constraints and define variables for the dimension constraints.
- You can test editing the sketch with the Dimension Table function.
- Variables are not required if there is only one cross-section size of the profile.
- Select the context-sensitive
 OK, and select Cross Section as the operation.
OK, and select Cross Section as the operation. - Add density to the model if the density differs from the default material and you want the weight calculated for the model to be correct.
- Part | Tools |
 Material.
Material.- Select the Mass tab.
- Enter into Density field: Density kg/m3.
- OK.
- Specify the default density: File >
 System Preferences > Mechanical Engineering > Mechanical tab > > Density.
System Preferences > Mechanical Engineering > Mechanical tab > > Density.- The default density defined by the software provider is the density of steel: 7850 kg/m3.
- Part | Tools |
- Add rendering material if you want the profile to look real.
- Select the following contextual function: Rendering > Change Material.
- Click Browse
- Browse and select the desired rendering material.
- Select OK to exit the menus.
- Save the cross section to the feature library
- Select the context-sensitive function: Save to Library >As Profile.
- For more details, see: Save a Profile Feature in the Library
Example of profile cross-section sketching