Create Tangential Faces
Advanced Face Modeling Package
General
- This feature is enabled if you have the Advanced Face Modeling Functions add-on option.
- The face selected with the function is made a tangential face to the faces surrounding it.
- If necessary, you can select one or more face edge lines to which tangentiality is added. This creates a sharp corner at the other edge lines.
- If you do not select any face edge lines, the face will be tangential to all edge lines.
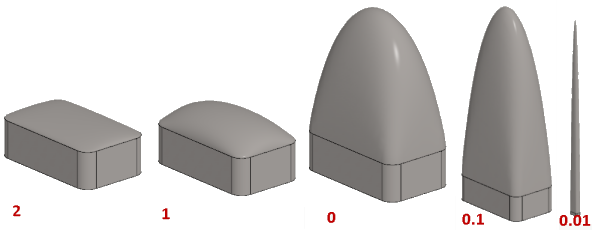
- The higher the flattening, the lower the shape.
- Zero represents kind of a default value.
- The suitable value is determined experimentally and depends on the shape. For example, try values between 0.1 and 2.
Create a Tangential Face
- Select the ribbon bar function Part | Faces |
 Create Tangential Faces or
Create Tangential Faces or- Import | Faces |
 Create Tangential Faces.
Create Tangential Faces.
- Import | Faces |
- Click a face or faces.
- Select Confirm (Confirm = V key, middle mouse button or the context-sensitive function
 OK.)
OK.)- The program opens the Create Tangential Face dialog box.
- Define the tangential face data in the dialog box.
- Enter flattening.
- Try the default value 0.
- Change the factor moderately, if necessary.
- Invert the face direction, if necessary
- Adjust the maximum number of spans, if necessary.
- Tangential geometry
- Select the edge lines of the face where tangency takes place.
 If you do not select edge lines, then tangency occurs at all edges.
If you do not select edge lines, then tangency occurs at all edges.
- If necessary, select the guide curve lines controlling the tangency
- Enter flattening.
- Click Apply to see what kind of face the program creates with the values you enter.
- If necessary, you can use the buttons to affect the faces to be replaced, the edges of the tangency face and the guide curves:
- Add.
- Change.
- Delete.
- Select OK.
Editing the selected face into a tangential face
- Select one or more faces in a part model.
- Hold down the Ctrl key if you select more than one face.
- Select the context-sensitive function
 Faces>
Faces>  Make Tangential.
Make Tangential.- The program opens the Create Tangential Face dialog box.
- Continue as above, steps 4...7.
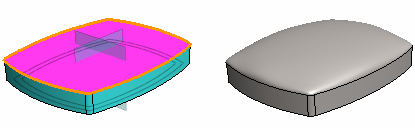
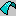
Example 1
Comparison of the tangential face of a sharp-cornered part and a part with corners rounded.
- The flattening is 0 (zero) in both.
- The example shows that the function is applicable mainly only to faces with non-sharp corners.
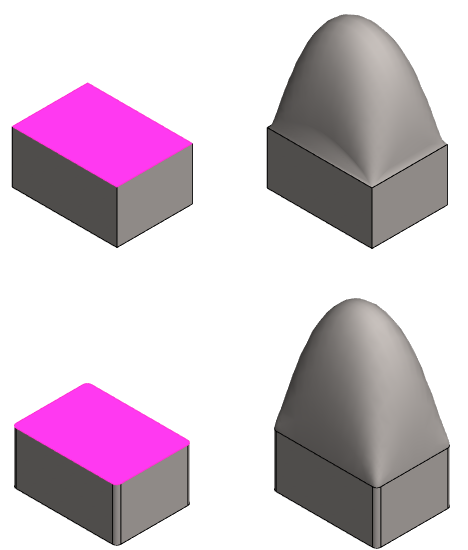
Example 2
Comparison when tangential geometry is or is not selected
- No tangential edge is selected in the upper image.
- In the lower image, one line (yellow) is selected as the tangential edge line.
- The flattening is 0 (zero) in both.
Example 3
- In the image, different tangency factors have been used for the same cross section.