Feature Pattern on a Cylinder Face
Starting point
The feature to be patterned is modeled on a cylinder or cone surface.
The Ribbon Bar Function
- On the
 tab, in the Tools group, click
tab, in the Tools group, click  Pattern.
Pattern. - Select the surface from the feature, from which you create the pattern.
- Define the feature pattern properties in the dialog box.
 Feature Pattern Data
Feature Pattern Data- Note that
 Polar is selected.
Polar is selected. - If you want the pattern to have more than one circle, enter:
- The number in the length direction and
- The Delta of the circles or the distance between the furthest circles (=Length) in the length direction.
- Enter the number of pattern members on the circle.
- Enter the angle or length of the pattern members on the circle.
- Angle: 360= the pattern is positioned evenly around the cylinder, 180= the pattern is positioned on the half of the cylinder.
- Delta is the angle between two features on the cylinder face.
- Note that
- Confirm the data in the dialog box by clicking OK.
- If you specified more than one as the number in length direction, place the auxiliary geometry sketch that controls the feature.
- This allows you to determine which direction the other circles come in relation to the original feature.
- Select the contextual
 OK
OK
The Context-Sensitive Function
This function allows you to select multiple features at once and create a pattern of them all.
- Select the parent feature from a part as follows:
- Select one or mode Boss or Cutout operation from the part's feature tree.
- In addition to these, you can choose a rounding or bevel that is connected to the above selected features.
- Select on or more face from the part. Select more than one feature by holding down the Ctrl key while clicking with the left mouse button.
- If you want to create a feature pattern from a rounding or a bevel, you must also include the feature to whose geometry the rounding/bevel has been added.
- Select the context-sensitive function Feature Pattern.
- Steps 3 … 6, as above.
Example of a single-circle polar pattern
- Length direction, number: 1.
- The Length value in the length direction is irrelevant, because there will only be 1 circle.
- The number of pattern members on the circle: 12.
- The angle is 360, i.e. the features are added on the entire cylinder surface.
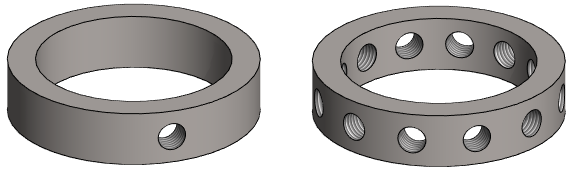
Example of a multi-circle pattern
- Length direction, number: 3.
- The distance between the circles is given to the Delta value in the length direction.
- The auxiliary geometry of the pattern is so positioned that it directs the circles upwards (middle image).
- The number of pattern members on the circle: 12.
- The angle is 360, i.e. the features are added on the entire cylinder surface.

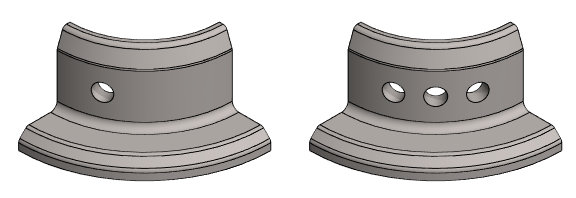
Example of a pattern set only on part of the circle
- Length direction, number: 1.
- The Length value in the length direction is irrelevant, because there will only be 1 circle.
- Direction: Counterclockwise
- The number of pattern members on the circle: 3.
- Angle: 40 (distance between the most extreme members of the pattern).